-
[프로그래머스] 프린터알고리즘/프로그래머스 2021. 7. 19. 14:42
풀이
이 문제는 크게 두 가지 방법으로 풀 수 있는 것 같습니다. 효율성이나 성능을 고려했을 때 반복문을 줄이는 게 좋다고 생각합니다. 이 관점에서, 우선순위 큐를 사용하면 알고리즘 헤더의 max_element를 매번 사용하지 않아도 되기 때문에 빠르고 효율이 좋습니다. pair을 연습해볼 수도 있어서 좋습니다.
코드1
#include <string> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; int solution(vector<int> priorities, int location) { int answer = 1; queue<pair<int, int>> index_value_q; priority_queue<int> pq; for (int i = 0; i < priorities.size(); ++i) { index_value_q.push({ i, priorities[i] }); pq.push(priorities[i]); } while (!pq.empty()) { auto [index, value] = index_value_q.front(); if (pq.top() == value) { if (location == index) return answer; else { ++answer; pq.pop(); index_value_q.pop(); } } else { index_value_q.push({ index, value }); index_value_q.pop(); } } }우선 순위 큐를 이용해 정렬을 해놓은 상태에서, 큐의 인덱스와 값을 같이 검사합니다. location에 해당하는 인덱스를 찾으면 바로 바로 반환합니다.
코드2
#include <string> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; int solution(vector<int> priorities, int location) { vector<int> numbers; queue<int> index_queue; for (size_t i = 0; i < priorities.size(); ++i) index_queue.push(i); while (!index_queue.empty()) { int index = index_queue.front(); index_queue.pop(); if (*max_element(begin(priorities), end(priorities)) != priorities[index]) index_queue.push(index); else { priorities[index] = 0; numbers.push_back(index); } } for (size_t i = 0; i < numbers.size(); ++i) if (numbers[i] == location) return i + 1; }max_element의 시간 복잡도는 max(N-1,0)입니다. 답을 탐색하는 과정에서 반복문도 한 번 더 돌려야 하기 때문에 첫 번째 코드보다 조금 느릴 수밖에 없습니다.
두 코드 모두 대부분 0.01ms가 많이 뜨지만 두 번째 코드에서 0.04ms가 뜨는 것이 첫 번째 코드에선 0.02ms가 나옵니다. 테스트의 최악 케이스에서 두 배의 성능 차이입니다.
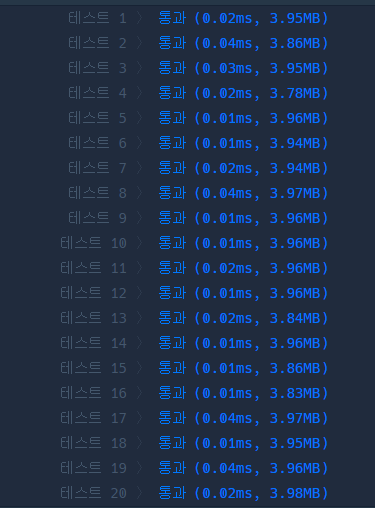
코드1 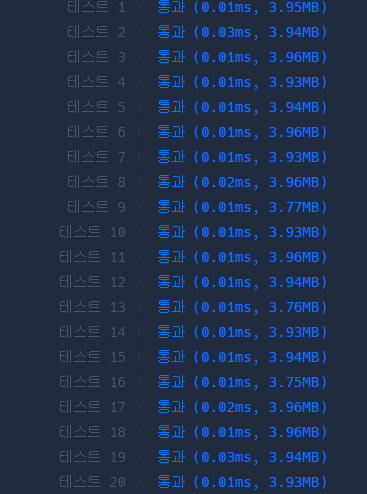
코드2 '알고리즘 > 프로그래머스' 카테고리의 다른 글
[프로그래머스] 단체사진 찍기 (0) 2021.07.25 [프로그래머스] 게임 맵 최단거리 (0) 2021.07.21 [프로그래머스] 오픈 채팅방 (0) 2021.07.19 [프로그래머스] 문자열 압축 (0) 2021.07.12 [프로그래머스] 가장 큰 정사각형 찾기 (0) 2021.07.11